



Building information modelling (BIM) is a popular information handling process. Despite its potential, the utilization in construction phase is very limited due to the lack of interaction between real and virtual worlds. As technologies evolve, so does our nature of imagining and visualizing something. Construction design is heavily dependent upon visualization, so it is no wonder that new data visualization technologies like AR and VR would influence and enhance BIM (Building Information Modelling) in leaps and bounds.
Introducing Augmented/ Virtual/Mixed Reality into BIM is believed to greatly increase the utilization of BIM in construction phase. Of these, AR (Augmented Reality) was chosen as the primary visualization tool, as it had the least utilization of hardware (mobile or tablet is sufficient) and the most scope in terms of utilizing BIM in the traditional construction process, over Virtual Reality or Augmented Reality creates a layer of the model over the On-site or real world scenario.
This case study demonstrates this technology which was implemented at IIT Bhilai project.
This Project comprises the construction of the Permanent campus of IIT with 3 Design packages: DP1 (Academic Zone), DP2 (Hostel Zone) and DP3 (Residential Zone).
The software adopted for the federation and interaction with BIM model were: Revit (.rvt), Navisworks (.nwd, .nwc) and IFC (Industry Foundation Class). For visualisation of the BIM model in Augmented Reality, Trimble Connect AR was chosen as the mobile application.
Project Chosen: IIT Bhilai
Building Name: Health Center


“AR is an easy to use, mobile friendly technology that can aid utilization of BIM in construction phase”.
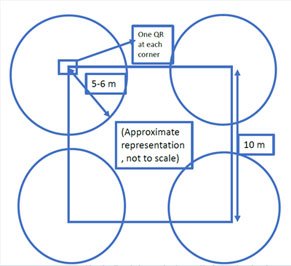
For the purpose of implementation of AR/VR technology in BIM, several Use Case scenarios were identified. Using a survey questionnaire, the preferred software and Use Cases with most potential were ascertained. Out of these, Interface management wherein AR allows a team to collectively experience BIM data interwoven with built environment i.e. superimposing of virtual model over real world and Quality Inspection was identified and chosen for the implementation use case. The Workflow development involved the federation and upload of the particular BIM models onto the Trimble server and further visualizing it on the mobile app and utilizing various features within the application. The implementation of the Workflow thus created, was executed by demonstration of the app live On-site for the Execution team.




"AR in BIM has created many widespread applications. The merging of virtual model and real world creating a mixed reality,
improving the capability of visualization, will no doubt revolutionize the way we see construction today."
Traditionally Quality Inspection is carried out before and after the execution of specific activities along with a predefined checklist for concurrence. One of the key check points is the reference to Design information/ drawings and ensure the execution is carried out as per Design intent. One of the challenge here is to refer to multiple Drawings (Sections, Elevations, coordinated layouts, etc) to understand the Design intent and any missing information during this stage would delay the Inspection process and can impact the subsequent activities. So, utilizing AR would allow for access to complete activity specific information in a single view over mobile device.

“AR technology can give huge value benefit during execution at site. The best way to leverage this technology is by integrating this in our Execution method statement as a mandatory step”.
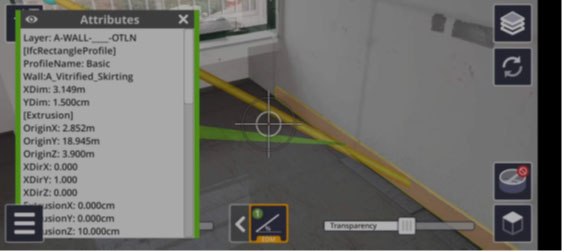
Interface management being one of the critical activities for successful closure of activities without rework. It is crucial to ensure the availability of relevant information for better Interface management. AR technology would allow the access to multi-disciplinary 3D model information that could be visualized over mobile devices


On site changes as inevitable because of the complex coordination challenges. It is important to capture such changes in a proper documented way to further record and submit the As Built information to client. Traditionally, this is done using Red line markups on drawings along with relevant photographs for reference. However, there are many instances where data mismatch and incomplete information would be populated, leading to incorrect output. AR technology helps in visualizing the design intent and the actual constructed form at the same time and allows the user to capture information on the deviations using markups and snapshots in the same view. This gives more clarity on the deviation and helps the team to update As Built drawings more accurately.
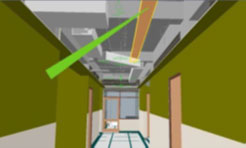

Cable tray has been placed below the HVAC duct due to on site cable pulling constraints. However, design intent was to place the cable tray above the duct. By super imposing the Design model on the actual construction view, the required deviation was easily captured and recorded for further reference and update.

“BIM-AR enabled workshops with field staff helps in better sequencing of the floor activities. Also, its usage across the construction phase simplifies the capturing of As-built information for facility handing over process.”